

It examined why we can be in a state of disequilibrium in the macro economy. In 1936, J.M.Keynes produced his The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money this examined why the depression was lasting so long. Classical economics didn’t really have an explanation for this dis-equilibrium, which from a micro perspective, shouldn’t occur. There was high unemployment, output was below capacity, and there was a state of disequilibrium. In the 1930s, economies were clearly not in equilibrium. Great Depression and birth of Macroeconomics Before, the 1930s, there wasn’t really a separate branch of economics called macroeconomics. For a long time, it was assumed that the macro economy behaved in the same way as micro economic analysis. If demand increases faster than supply, this causes price to rise, and firms respond by increasing supply. But, there are other differences.Ĭlassical economic analysis assumes that markets return to equilibrium (S=D).
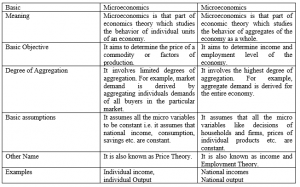
The main difference is that micro looks at small segments and macro looks at the whole economy. Micro economics tends to work from theory first – though this is not always the case.ĭifferences between microeconomics and macroeconomics Macro economics places greater emphasis on empirical data and trying to explain it.Keynesian, Monetarist, Austrian, Real Business cycle e.t.c). There are different schools of macro economics offering different explanations (e.g. There is little debate about the basic principles of micro-economics.In macro economics, the economy may be in a state of disequilibrium (boom or recession) for a longer period. Microeconomics works on the principle that markets soon create equilibrium.Small segment of economy vs whole aggregate economy.The main differences between micro and macro economics Macro diagrams are based on the same principles as micro diagrams we just look at Real GDP rather than quantity and Inflation rather than Price Level (PL).


Reasons for inflation and unemployment.what effect does interest rates have on the whole economy? Externalities arising from production and consumption.Supply and demand in individual markets.It looks at ‘aggregate’ variables, such as aggregate demand, national output and inflation. Macro economics is the study of the whole economy.It looks at issues such as consumer behaviour, individual labour markets, and the theory of firms. Microeconomics is the study of particular markets, and segments of the economy.Readers Question: Could you differentiate between micro economics and macro economics?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
